✓ Fact Checked 🕓
❙ Our team of writers, editors, and medical experts rigorously evaluates each article to ensure the information is accurate and exclusively cites reputable sources.
❙ We regularly assess how the content in this article aligns with current scientific literature and expert recommendations in order to provide the most up-to-date research.
Venlafaxine and Xerostomia – A Comprehensive Guide
Depression, anxiety and panic disorders are complex conditions that significantly alter a person’s psychological and physical well-being. These disorders are closely linked to imbalances in the levels of hormones and neurotransmitters, such as cortisol, serotonin, and norepinephrine. Depression manifests through a persistently low mood, while anxiety is characterized by excessive fear or worry. Panic disorders, on the other hand, include sudden episodes of intense fear with no apparent cause.
Venlafaxine: More than an Antidepressant
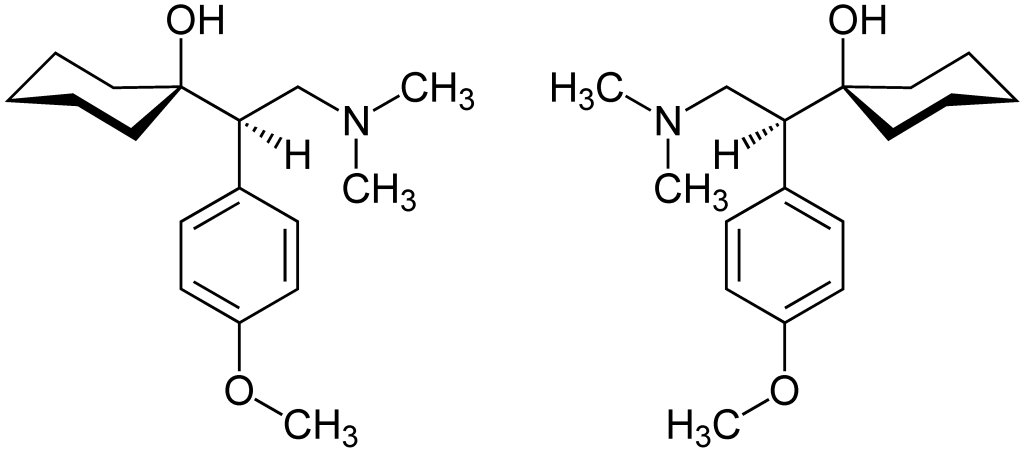

Venlafaxine is an effective medication in the treatment of these conditions. Its mechanism of action focuses on the regulation of neurotransmitters in the brain, especially serotonin and norepinephrine, which help improve mood and relieve anxiety. It is crucial to follow medical instructions regarding dosage and not stop treatment abruptly. Additionally, it is important to be aware of possible side effects, such as xerostomia.
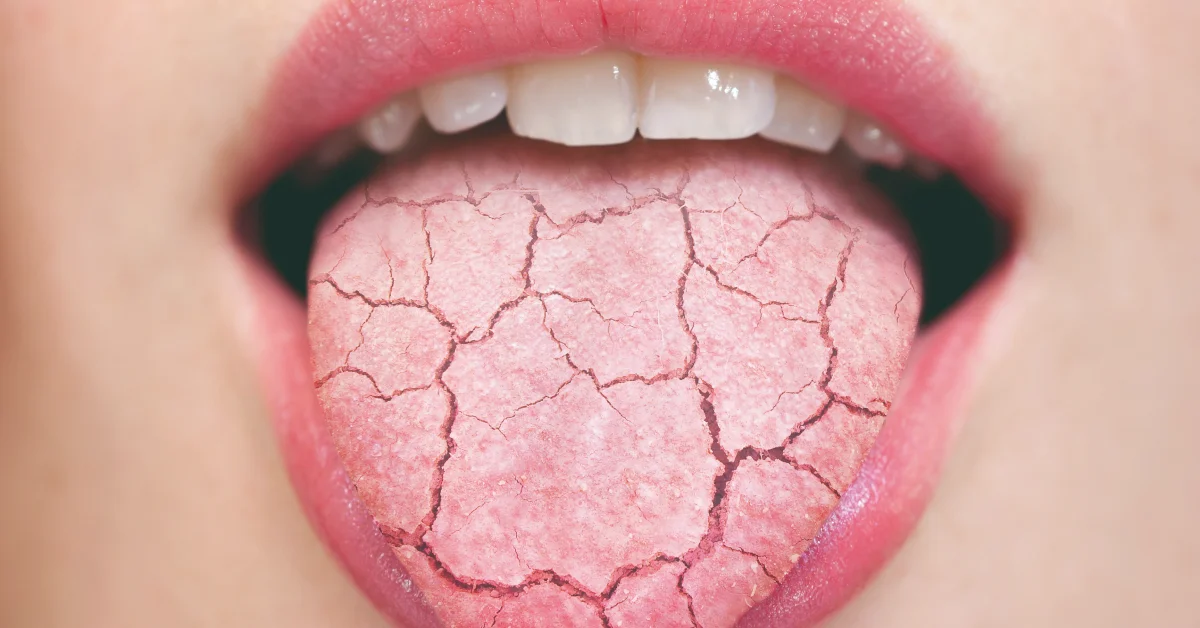
Xerostomia: More than Dry Mouth
Xerostomia, commonly known as dry mouth, goes beyond a simple discomfort. It can have a significant impact on oral and general health, leading to problems such as difficulties chewing, swallowing, and speaking, and an increased risk of cavities and gum disease. Xerostomia is particularly concerning in older patients, where oral health is critical to nutrition and overall quality of life.
Saliva: A Key Element in Oral Health
Saliva plays a vital role in oral health, not only in digestion but also in protecting teeth and gums. It facilitates chewing, swallowing, and speaking and acts as a defense agent against bacteria and fungi. Adequate salivary flow is essential to maintaining a healthy balance in the mouth. Additionally, it performs functions such as:
● It lubricates the oral cavity, protecting it from irritants and reducing acid erosion which leads to dental cavities.
● It helps form a biofilm, which protects the tooth surface.
● It acts as a vehicle for nutrients and digestive enzymes, helping in the preparation of the bolus
● It helps with chewing, swallowing, and speaking.
● It acts as a line of defense against mechanical, chemical, and infectious attacks by protecting the oral environment from bacteria and fungi.
In general, a healthy individual can produce between 500 ml to 1000 ml of saliva daily, which helps start the digestive process and improve taste perception.
Comprehensive Management of Xerostomia

To treat xerostomia, it is essential to take a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, such as increasing water intake and avoiding irritating substances such as tobacco and alcohol. The use of specific products such as artificial saliva, special mouthwashes, and sugar-free gum can be beneficial. Regular consultation with a dentist is crucial to monitoring and managing any changes in oral health.
There are different treatment alternatives for the management of xerostomia, some of which are mentioned below:
● Drink water regularly or suck on ice chips (relieves dryness, facilitates swallowing, hydrates tissues, and cleanses the mouth).
● Chew sugarless gum or suck on sugarless hard candy.
● Avoid tobacco, alcohol, and caffeinated drinks because they can make your mouth dry.
● Using mouthwashes, gels, sprays, and artificial saliva can help reduce discomfort and temporarily improve function (if they do not contain alcohol or detergent, but they may contain antimicrobial agents)
● Breathe through your nose, not your mouth.
● Brush your teeth twice a day, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly. Having a dry mouth can increase the risk of cavities.
● Vitamin C tablets have also been recommended to stimulate salivary flow, as they act as a reducing agent, breaking disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in proteins, leading to a decrease in saliva viscosity.
● Talk to your doctor or dentist about over-the-counter or prescription medications to treat dry mouth.
● Talk to your treating doctor to adjust the dose or change treatment if it is the result of a side effect.
Prevention and Oral Care in Case of Xerostomia

In addition to treatments, it is important to focus on prevention and ongoing oral health care. This includes practices such as regular use of fluoride toothpaste, fluoride mouthwashes, and regular visits to the dentist for checkups and professional cleanings. These measures help minimize the risks associated with dry mouth and keep the mouth in optimal condition. Therefore, it is important that, in the event of any health condition, you maintain good oral hygiene, such as:
● Avoid sugary and acidic foods and drinks: they increase the risk of cavities.
● Brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste: Always ask the dentist if it is favorable and which would be the most appropriate.
● Use a fluoride mouthwash or fluoride gel before going to bed. Sometimes a custom fluoride applicator (made by your dentist) can make it more effective.
● Visit your dentist at least twice a year to detect and treat cavities or any other dental problem.
Conclusion
Venlafaxine, an effective treatment for psychiatric disorders, can cause xerostomia, a side effect that affects oral health. Comprehensive management of this symptom is essential, focusing on both mental and oral health, through oral hygiene practices and collaboration with health professionals. Thus, a complete treatment is ensured that improves the patient’s quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What helps with dry mouth caused by antidepressants?
a. Drink water regularly or suck on ice cubes.
b. Chewing sugarless gum or sucking on sugarless hard candy.
c. Avoid tobacco, alcohol and caffeinated drinks, as they can increase dry mouth.
d. Breathe through your nose, not through your mouth.
e. Brush your teeth twice a day, floss daily, and visit the dentist regularly.
What is a common side effect of venlafaxine?
You may experience nausea, sleepiness, dizziness, dry mouth, constipation, decreased appetite, blurred vision, restlessness, difficulty sleeping, excessive sweating, or frequent yawning. If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, inform your doctor immediately.
How to reduce the side effects of venlafaxine?
It is advisable to take venlafaxine early in the morning. Add more fiber to your diet, including fruits, fresh vegetables and grains, and make sure you drink enough water. Also, get regular exercise, such as walking or running daily. If these measures are not effective, consult your pharmacist or doctor.
What is the reason that antidepressants cause dry mouth?
These medications may reduce salivary gland function, change the perception of dry mouth, or both. Older patients tend to be at higher risk of experiencing dry mouth as a side effect of these drugs, with a more notable decline in salivary gland function as compared to younger adults.
Share:
References
1. WebMD. (2017). Venlafaxine Oral: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing. https://www.webmd.com//drugs/2/drug-4870-1047/venlafaxine-oral/venlafaxine-sustained-release-oral/details
2. Mayo Clinic. (Jun, 2023). Depresión: apoyar a un familiar o a un amigo. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/depression/in-depth/depression/art-20045943
3. MedlinePlus. Anxiety. Bethesda (MD): Biblioteca Nacional de Medicina (EE. UU.). https://medlineplus.gov/anxiety.html
4. NHS. (Feb, 2022). Venlafaxine: an antidepressant. https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/venlafaxine/
5. Mayo Clinic.(Sep, 2019). Antidepresivos: Recibe consejos para lidiar con los efectos secundarios. https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/depression/in-depth/antidepressants/art-20049305
6. NIH. (Jun, 2019). Dry Mouth. National Institute of Dental And Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/dry-mouth